Numbers
What are integers?
Integers are numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero. They include the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, …), the negative numbers (-1, -2, -3, …), and zero.
The set of integers Z = { 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, ±4, …}
Whole numbers
Whole numbers are the natural numbers and zero. They are the numbers that we use to count things. For example, the number of students in your class is a whole number. Negative numbers are not considered part of the set of whole numbers.
The set of whole numbers W = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
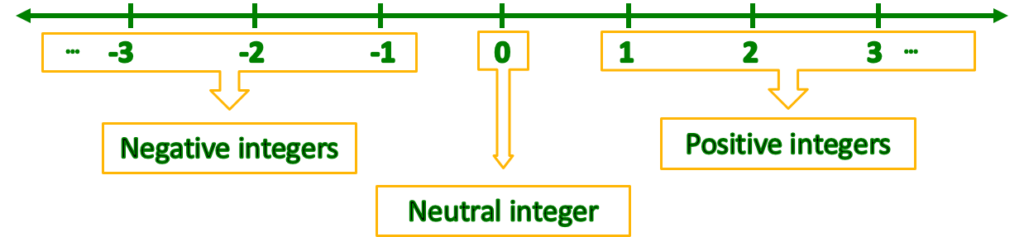
Number line
We can use a number line to represent integers. The number line is a line that has all the integers plotted on it. The numbers are arranged in order, with the positive numbers to the right of zero and the negative numbers to the left of zero.
Absolute value
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero. For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3. The absolute value of -3 is denoted by |-3|. The absolute value of a number is always positive.
Here are some more examples of integers:
- Positive integers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …
- Negative integers: -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, …
- Neutral integer: 0
- Whole numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …
- The absolute value of -4 is denoted by|-4| which is equal to 4.
- The absolute value of 4 is denoted by|4| which is equal to 4.
